Since its launch, Ethereum has become the most widely used blockchain protocol in the crypto world and its native token ETH has also grown into one of the most popular tokens, second only to BTC in market cap.
What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized, open source blockchain with smart contract functionality.
To simply put it, it is a blockchain platform where anyone can set up an application on the network at their own will. Similar to the software for Windows and Android systems on the internet, the protocol was designed to have a special scripting language, enabling people to develop applications as they desire. As it’s powered by blockchain technology, it is highly decentralized in nature, marking it quite different from the abovementioned systems. On the network, any alteration to the entire system protocol needs to be determined at large by community members, rather than a single entity or individual. Furthermore, all applications developed on the network completely belong to individual users including permission and data, and community consent is a must before any program modification.
As many know, Bitcoin is the first application of blockchain technology and its birth brought blockchain technology into zeitgeist of the general public for the first time. If Bitcoin is the origin of blockchain, it can be said that Ethereum is the further evolution of blockchain. As Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum said, Ethereum is the platform for the next generation cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications. Hance, Ethereum is also regarded as a second generation blockchain and its birth also marks beginning of the blockchain 2.0 stage.

Origin of Ethereum
Ethereum was a concept proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2013, who was a programmer involved in the development of the Bitcoin community. During the development, he found some restrictions on Bitcoin scripting language, hoping to design an evolution of Bitcoin beyond the scripting language in a Turing complete programming environment, enabling people to develop programs. However, his ideas were declined by the Bitcoin development community, so he decided to develop a new generation of blockchain himself, which is capable of running decentralized applications.
In 2014, he conducted a public crowd sale to finance the project. On July 30, 2015, Ethereum was formally announced.
Main Features of Ethereum
Different from the attribute of Bitcoin as a currency, Ethereum pays more attention to its platform attributes. It’s more of an operating system of the blockchain version from its positioning. If Bitcoin’s development may disrupt the role of PayPal and centralized banks, Ethereum’s growth may lead to Internet third parties being replaced by blockchain, especially third parties dedicated to data storage.
Ethereum’s most significant technical contribution is the creation of smart contracts, which are the key to supporting Ethereum to achieve its vision. With smart contracts, people are allowed to design operations on the protocol that can be automatically executed according to the pre-set conditions. Users can utilize the complete programming language on the Ethereum blockchain and execute more complex smart contracts on the network without need of relying on any third party.
Ether (ETH)
Ether (ETH) is the native token of Ethereum blockchain and is also the settlement token of the network, namely that ETH is used for the settlements of payments for running Ethereum’s smart contracts, on-chain transaction fees and mining rewards.
Token name: Ether
Token symbol: ETH
Issuing Date: July 30, 2015
Circulating Supply: No limits
Comparison of ETH and BTC
| Category | ETH | BTC |
| Issuing date | 2014 | 2009 |
| Founder | Vitalik Buterin | Satoshi Nakamoto |
| Consensus mechanism | PoW+PoS | PoW |
| Circulating supply | No limits | Around 21 million |
| Block time | Around 12~14 seconds | Around 10 minutes |
| Genesis block reward | 5 ETH | 50 BTC |
| Current block reward | 2 ETH | 6.25 BTC |
| Halving time | No halving mechanism | Halve every 21 million blocks (around 4 years) |
Ethereum’s Evolution
The Ethereum project is divided into 4 stages of development, which are Frontier, Homestead, Metropolis and Serenity, with the first three stages called Ethereum 1.0 and the last stage known as Ethereum 2.0. Please see below for details:
- 2013 – Release of Ethereum’s White Paper
On Nov. 27, 2013, Vitalik Buterin released a white paper conceptualizing the “next-generation smart contract and decentralized application platform” known as “Ethereum”.
- 2014 – Release of Yellow Paper
On Apr. 1, 2014, Ethereum’s co-founder Gavin Wood published the “Yellow Paper” based on the technical implementation of the Ethereum protocol.
- 2014-Public Crowd Sale
A 42-day public crowd sale of ETH was held between July 22 and September 2, 2014.
- 2015-Olympic Test Network
On May 9, 2015, Ethereum launched the Olympic Test Network — the ninth and final proof of concept (PoC) open testnet, available to developers to explore what the Ethereum blockchain would look like once released.
The 1st stage - Frontier
- 2015 – Frontier Upgrade
On July 30, 2015, the Ethereum Frontier Network was released at the block height of 0. As the most primitive form of Ethereum, Frontier supported a few utility features and was mainly aimed at technical users, professional developers. In the phase, miners can install and run the network on their PCs. When they successfully mine a block into existence on the Ethereum blockchain, they receive a reward of 5 ETH per block. During the first few days of Frontier’s existence, the gas limit per block was hardcoded at 5,000 gas. Canary contracts were included into Frontier to notify users that a particular chain was bad or vulnerable.
- 2015-Frontier Thawing Upgrade
On Sep. 7, the frontier thawing fork was completed at the block height of 200,000, with the difficulty bomb mechanism included into Ethereum’s architecture. The first hard fork of Ethereum lifted the 5,000 gas limit per block and set the default gas price to 51 gwei. With the fork, Ethereum enabled the transaction function - the 21,000 gas limit necessary to process one basic transaction per block.
The 2nd stage – Homestead
- 2016 – Homestead Upgrade
The Homestead upgrade was the first planned hard fork of the Ethereum network and was implemented on May 14, 2016 with block number 1,150,000. Overall, the Homestead upgrade included three major improvements to Ethereum. First, it removed the canary contract functionality, removing that point of centralization on the network. Second, it introduced new codes in Solidity, the programming language used on Ethereum. Last, it introduced the Mist wallet, which allowed users to hold/transact ETH and write/deploy smart contracts.
- 2016-DAO Fork
In June, the DAO was hacked. Ethereum implemented the DAO fork at block 1,920,000. The hard fork, however, was contentious in the Ethereum community, leading to the split of the network into the Ethereum Classic and the Ethereum blockchain.
- 2016 - Tangerine Whistle Upgrade
Tangerine Whistle, a small unplanned fork took place on Oct. 18, 2016 at block 2,463,000. The fork aimed to deal with DoS attacks, increasing the cost of virtual machine opcodes
- 2016 - Spurious Dragon Upgrade
Following Tangerine Whistle, Spurious Dragon is the second hard fork of the two-round hard fork response to the DoS attacks on the Ethereum network, which was implemented on Nov. 22, 2016 at block 2,675,000, which included four proposals related to fixing unwanted behaviors: simply replay attack protection, EXP cost increase, state tree clearing, contract code size limit.
The 3rd stage – Metropolis
- 2017 - Byzantium Upgrade
Byzantium went live on Oct. 16, 2017 at block 4,370,000, which was the name given to the third planned stage of Ethereum. It contained a wide variety of changes, including reduction of block reward from 5 ETH to 3 ETH, the delay of the difficulty bomb by 1 year, a new ability to call other smart contracts and inclusion of some cryptography methods to allow for expansion in layer 2.
- 2019 - Constantinople Upgrade
The second part of the Metropolis upgrade, named Constantinople, went live on Feb. 28, 2019 at block 7,280,000. The fork delays the implementation of the Difficulty Bomb for another twelve months and reduced block reward from 5 ETH to 2 ETH. Other changes included the optimization of the EVM data storage gas cost.
- 2019 -Istanbul Upgrade
Ethereum’s Istanbul went live on Dec. 8, 2019 at block number 9,069,000, including upgrades to Ethereum that will optimize the EVM data storage gas cost and improve performance of SNARK and STARK-based layer 2 solutions.
- 2020-Muir Glacier Upgrade
The Muir Glacier upgrade took place on Jun. 2, 2020 at block 9,200,000, with the aim to delay the difficulty bomb.
The 4th stage – Serenity
- 2020-Deploy of staking contract
The Muir Glacier upgrade activated on the mainnet on Oct. 14, 2020 at Block 11,052,984. It formally introduced the staking deposit contract into the Ethereum ecosystem, laying a solid foundation for Eth 2.0 initiative.
- 2020-Beacon Chain
Beacon Chain upgrade launched on Dec. 1, 2020.
- 2021-Berlin Upgrade
The Berlin hard fork upgrade went live on April 15, 2021 at block 12,244,000, including changes that optimize the gas cost of EVM opcodes and increase support for multiple transaction types.
- 2021-London Upgrade
The London upgrade activated on Aug. 15, 2021 at block 12,965,000. It introduced the EIP-1559 to completely revolutionize the way the fee market works on the Ethereum network
- 2021-Altair Upgrade
On Oct. 27, at epoch 74240, the Altair Beacon Chain upgrade activated on the Ethereum mainnet. As the first scheduled upgrade of the beacon chain, the hard fork activates light clients and offers support for sync committees and increases the inactivity and slashing penalty fees.
- 2021-Arrow Glacier Upgrade
The Arrow Glacier activated on Dec. 9, 2021 at block 13,773,000 changed the parameters of the Ice Age/Difficulty Bomb, pushing it back until June 2022.
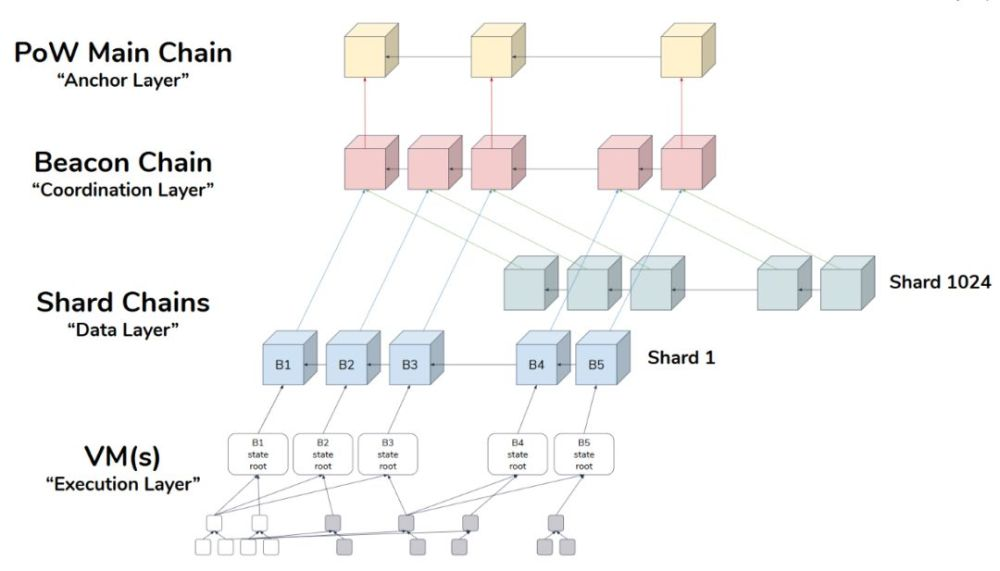
Presently, the Serenity stage is still in progress, with Beacon chain merging into the blockchain. Ethereum will mainly focus on shard chains, eWASM and continuous upgrades for its future development. It’s an immense and complicated process for the migration from the Eth 1.0 to the Eth 2.0, and will take several years for the blockchain to move from the PoW mining to the PoS mining.















